The Definitive Guide to Computer Ergonomics
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, many of us spend countless hours hunched over computers for work or leisure. As a result, it is essential to understand and implement proper computer workstation ergonomics to prevent discomfort and long-term health issues. This comprehensive blog post will guide you through setting up an ergonomically correct workstation that promotes health and well-being.
Key Considerations for Computer Ergonomics:
Desk Height and Organization
Your desk height should allow for comfortable typing and mouse use without causing you to hunch or raise your shoulders. If you’re using a fixed-height desk, adjust your chair height to achieve proper alignment. If possible, invest in a height-adjustable desk to easily transition between sitting and standing throughout the day. Keep frequently used items within easy reach to minimize excessive reaching or twisting.
Chair and Posture
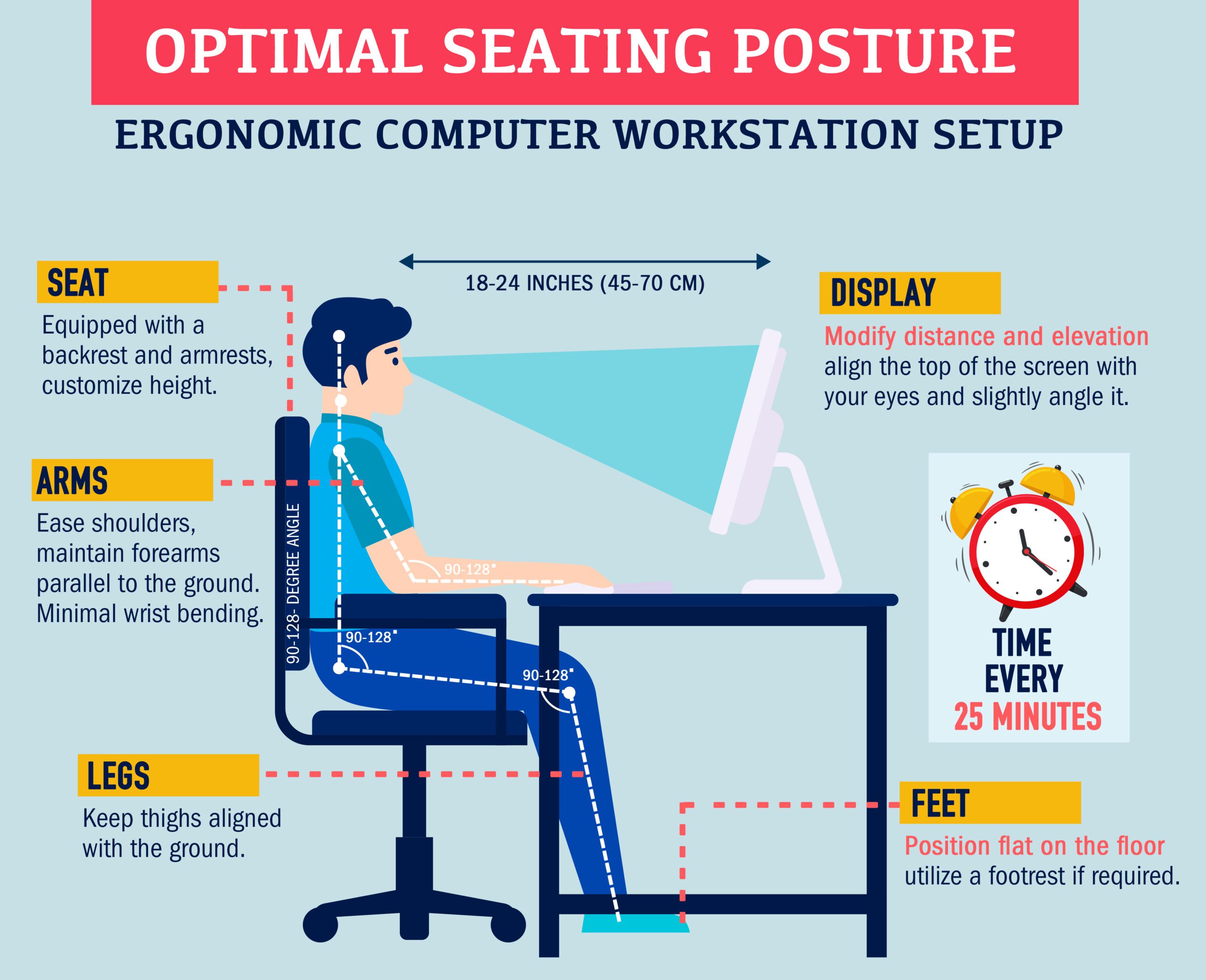
A good ergonomic chair is essential for maintaining proper posture and preventing back pain. Look for a chair that offers lumbar support, adjustable height, and armrests to accommodate your unique body proportions. Your feet should be flat on the ground, and your knees should be bent at a 90-degree angle. Sit back in your chair, maintaining the natural curve of your lower back, and avoid slouching or leaning forward.
Head and Neck Alignment
One of the most crucial aspects of proper ergonomics is head and neck alignment. According to Hedge, your head should be vertical to your neck to minimize strain on your neck, shoulders, and back[2]. To achieve this, position your computer monitor at eye level, directly in front of you, and at a comfortable distance to avoid tilting your head up, down, or to the side.
Monitor Position and Lighting
As mentioned earlier, your monitor should be at eye level and directly in front of you. Place it approximately an arm’s length away to prevent eye strain. Reduce glare by positioning your monitor perpendicular to windows and adjusting your screen brightness. Additionally, use appropriate ambient lighting to minimize eyestrain and avoid direct sunlight or bright overhead lights.
Keyboard and Mouse Placement
Repetitive typing and using a laptop’s touchpad or standard mouse can cause fatigue and pain in your fingers and wrists[1]. To counteract this, place your keyboard and mouse close to your body to maintain a relaxed posture. Keep your wrists straight and your elbows bent at a 90-degree angle. Additionally, consider using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse designed to reduce muscle strain and provide a more comfortable experience.
Ergonomic Keyboards
Ergonomic keyboards come in various designs, with split and curved models being among the most popular choices. Split keyboards divide the keys into two separate sections, allowing your hands and wrists to maintain a more natural position while typing. This design helps reduce strain on your wrists and fingers, minimizing the risk of repetitive stress injuries. Curved or contoured keyboards, on the other hand, feature a gently sloping design that follows the natural curve of your hands, providing a more comfortable typing experience. These keyboards can improve posture and reduce the likelihood of developing wrist and hand discomfort. Although it may take some time to adjust to these new keyboard layouts, the long-term benefits to your comfort and health make them worthwhile investments.
Ergonomic Mice
Similar to keyboards, ergonomic mice come in various designs aimed at enhancing comfort and reducing strain. Trackball mice, for example, feature a large ball that you manipulate with your fingers or palm to control the cursor. This design allows your hand to remain stationary, reducing wrist movement and minimizing strain. Vertical mice, another popular ergonomic option, position your hand in a handshake-like grip, promoting a more neutral wrist position and alleviating tension. As with ergonomic keyboards, there may be an initial learning curve as you adapt to these unique mice designs. However, the potential benefits to your comfort, health, and overall productivity make them a valuable addition to your workstation.
Taking Breaks and Staying Active
Even with a perfect ergonomic workstation, it’s essential to take regular breaks and stay active throughout the day. Stand up, stretch, and walk around for a few minutes every hour. This will help prevent muscle stiffness, promote blood circulation, and reduce the risk of developing repetitive stress injuries.
Diverse Chair Alternatives for Your Ergonomic Workstation
Having a comfortable and supportive chair is another vital aspect of proper computer workstation ergonomics. In this section, we will explore some popular alternatives to traditional ergonomic chairs, such as saddle seat chairs, medicine ball chairs, kneeling chairs, and standing desk chairs or stools.
Saddle Seat Chairs
Saddle seat chairs are designed to resemble a horse’s saddle, promoting an open hip angle and allowing your spine to maintain its natural curvature. These chairs encourage better posture by engaging your core muscles and minimizing lower back pressure. They also offer the benefit of improved circulation due to the open-angle seating position. Saddle seat chairs are ideal for those looking for a more active seating option and can be particularly helpful for individuals with lower back pain.
Medicine Ball Chairs
Medicine ball chairs, also known as stability ball chairs or exercise ball chairs, replace a traditional chair’s seat with an inflated exercise ball. This design encourages micro-movements and active sitting, which can help strengthen your core muscles, improve balance, and promote better posture. Medicine ball chairs are a great choice for those who want to incorporate some physical activity into their workday but should be used in moderation and alongside a traditional ergonomic chair for optimal support and comfort.
Kneeling Chairs
Kneeling chairs are designed to redistribute your weight from your lower back to your shins and promote a more upright posture. The forward-slanting seat and knee support pads gently tilt your pelvis forward, encouraging proper spinal alignment. Kneeling chairs can be an excellent option for individuals with lower back or tailbone pain, but it is essential to use them with a padded surface to avoid discomfort in your knees and shins.
Standing Desk Chairs and Stools
For those who use standing desks, standing desk chairs or stools can provide a comfortable and supportive seating option while maintaining an elevated position. These chairs often come with adjustable heights, allowing you to easily transition between sitting and standing throughout the day. Some models also feature a tilting seat, promoting an open hip angle and better spinal alignment.
Computer Ergonomics Conclusion
Proper computer workstation ergonomics are crucial for preventing discomfort, pain, and long-term health issues. By following the guidelines presented in this post, you can create a workspace that promotes productivity, health, and well-being. Prioritize your comfort and health by investing in ergonomic furniture, taking regular breaks, and implementing recommended practices.
In addition to these guidelines, engaging in a conversation with Dynamic Network Solutions can help identify other areas of improvement for workstation posture and general productivity. Our expertise in ergonomics and office productivity can provide personalized solutions and further enhance your working environment. Contact us today to ensure that you are taking all necessary steps to optimize your workstation and maintain a healthy, productive lifestyle.